Windows Set Up for C++
Guide to setting up the Windows operating system for C++ development.
DISCLAIMER: The University of Lethbridge is not responsible for the set-up of your machine, this is a guide set up by the ULSCU.
WARNING: Changing critical settings within the programs we are working on can damage your system. If you are unsure, start by making a backup so if something does go terribly wrong, you don’t lose your data.
Install MSYS2 Executable
In order to install the CPP compiler on your Windows machine, you will need to install the MSYS2 executable. It can be found here.
Once downloaded, run the executable and use the default location of C:\msys64 and finish the install. A new terminal window should open with the follow format in the first line of the terminal user@desktop UCRT64. If this window does not open, go to your start menu, then your program list. Your system might have a folder labeled MSYS2 or it might have a list of programs starting with MSYS2 followed by different endings like CLANGXX or MINGWXX where XX is 32 or 64. Open the MSYS2 UCRT64 terminal and update the terminal using pacman -Syu.
Using Pacman
Pacman is not used in any Windows package manager but MSYS2 is maintained in Linux and uses one of the Linux package managers for distribution. This would be the only place where it is used.
To install the gcc compiler run $ pacman -S mingw-w64-ucrt-x86_64-gcc pressing enter to keep installing when prompted. This command will save the compiler to the C:\msys64\usr\bin path. Keep this in mind for later.
Check Install
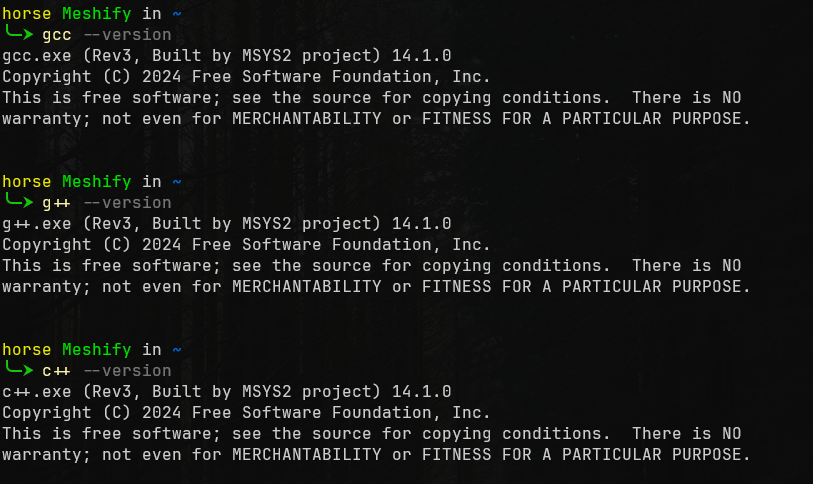
Now to check if it is installed. Open up your terminal of choice (I recommend Powershell 7) and try the following commands one at a time pressing enter after each one: gcc --version, g++ --version, and c++ --version.
Check if on Path
The output from each one should be the name of the program followed by the version and copyright information. If an error is showing or nothing at all, then it needs to be added to the PATH.
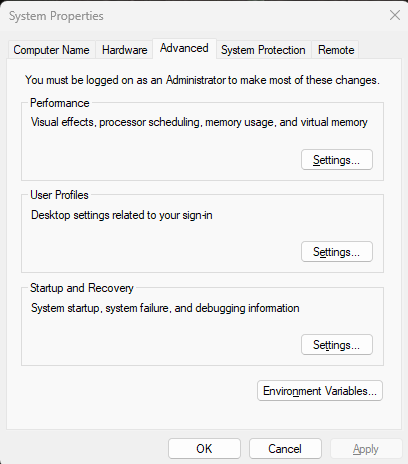
Adding programs to the PATH is fairly easy. All you need to know is the location of the information you need. It is usually located inside of the \bin folder where the program was saved. Open the start menu and type in Edit the system environment variables and press enter.
Edit Variables
A smaller window should open titled System Properties with the Advanced tab already open. Towards the bottom of the window there is a button called Environment Variables. Click it opening another window.
System Properties
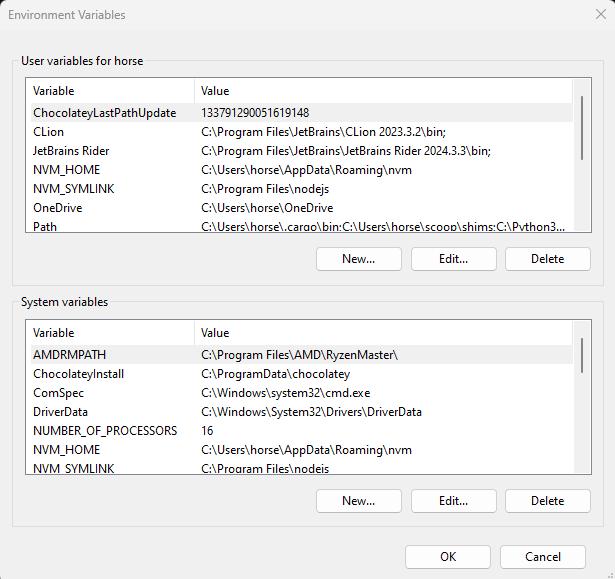
There will be two options to pick from. We want to use the bottom section called System Variables.
User or System Variables
Be careful in here since it can change how your system works or stop it from working!
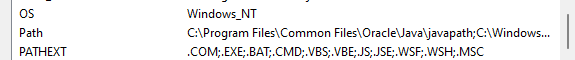
You will need to scroll down to where you see Path and click it once to highlight it and click edit.
System Path
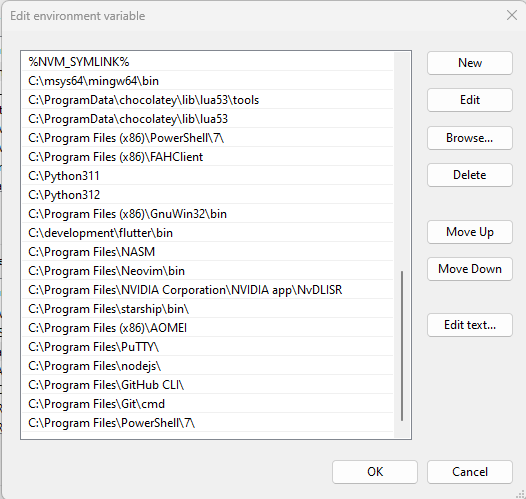
There should be a list of programs in this new window.
There should be a list of buttons on the right side. Click New and paste C:\msys64\usr\bin and click OK. Order does not matter here. We just want to make sure the system knows where to look for the program.
Edit System Variables
Close your current terminal session and open a new terminal to rerun the commands from earlier (gcc --version, g++ --version, and c++ --version). If they are still not working then you might also need to add C:\msys64\mingw64\bin to the PATH as well. This should fix any issues you might have. Close all of the Edit system environment windows by clicking OK. Now go run a simple C++ program to check if compiler is working!
1
2
3
4
5
6
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello World!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Issues / Feedback / Contributing
If you see any problems with these pages (incorrect information, misspelled words, incorrect formatting), please create an issue on the repo, or let one of the executives know.
If you have an idea for a resource or page that could be useful, please make a pull request so it can be added to the site, see more detail in the README.